Part I
Dear UGC NET Aspirants! As you all know there will be 5 Question based on Communication in General Paper 1 exam. This has been also observed that Question were mostly asked from definition of communication, information barriers of communication, communication models and theories and informal and formal communication differences.
In this blog we will cover the most important topics of Communication as below:
- Introduction to Communication
- Various definition
- Process of communication
- Forms and types of communication
- Communication models and theories
- Barriers to effective communication
- Organizational communication
- Formal communication channels and network Pro and Cons
- Organizational Communication channel network and Pro and Cons
Objective
After studying this blog , you should be able to: Understand the meaning and definition of business communication. Be able to know the objectives of communication Know the relevance of communication in an organisation and in management Understand the functions and importance of communication Know the scope of communication
Introduction to communication
Communication is defined as “the process of passing information and understanding from one person to another, it is essentially a bridge of meaning between people” All communication is essentially sharing of information or some message. Communication is the most important of our social activities.
We can classify communication as interpersonal, intrapersonal, group communication, Meta communication, upward, downward, lateral, diagonal, formal, informal, oral, written or non verbal communication.
Understand the functions and importance of communication
In terms of Business “Communication is an important requirement of every business. A businessman participates in the process of communication in many ways. For instance, he informs the consumer about his product, he motivate them to do the work or collects information about the progress of business etc.”
Three Simple Definitions
• Communication means sharing of information
• Communication is the giving and receiving of messages
• Communication is the transfer of information from one or more people to one or more other people
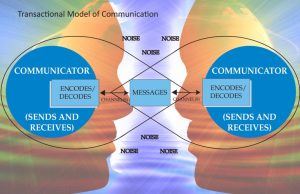
Meaning of Communication
The term communication is derived from the latin word “communis” or “communicare” which means to make common. Thus communication means to make common facts, information’s, thoughts and requirements. Communication therefore is the exchange of thoughts, message, information etc. by way of speech, signal or in writing.
Communication is two way process and works well with feedback, this helps to confirm that intended message has been successful.
Scholar Definition of communication
In order to understand further, many scholars has define the term such as
“Communication is the sum of all things, one person does when he wants to create understanding in the minds of another. It involves a systematic and continuous process of telling, listening and understanding.”
– Allen Louis
Communication has been defined “As the transfer of information from one person to another whether or not it elicits confidence.”
– Koontz and O’ Donell
“Communication is an exchange of facts, ideas, opinions or emotions by two or more persons.” – George Terry
“Communication is the process by which information is transmitted between individuals and/or organization so that an understanding response results”.
– By Peter Little
“Communication is an exchange of facts, ideas, opinions or emotions by two or more persons”.
– By W.H. New man and C.F. summer Jr.
There are many other comprehensive definition exist and touches all the aspects of communication process in general terms such as business communication, Organizational communication etc.
“Administrative communication is a process which involves the transmission and accurate replication of ideas ensured by feedback for the purpose of eliciting actions, which will accomplish organizational goals.”
Process of Communication
Communication is effective when a concise and clear message is delivered well, received successfully and understand fully. The process of communication has the following distinct components:
UGC NET Note for Communication Process
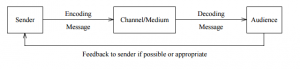
Communication-Process-Notes
Communication begins with an impulse (or motivation) to pass on a message made up of bits of information. In the process of encoding, units of information are selected and organized for transmission. Input is the sum of experiences that build up in the human brain or computer. Output is the encoded message transmitted by the information source (an individual person or group of people). The interpretation of the message is referred to as decoding. Feedback is the response, or message that the recipient (decoder) returns to the sender (encoder).
- Sender has an idea
- Sender encodes the idea
- Sender transmits the message through medium
- Receiver gets the message
- Receiver decodes the message
- Receiver sends feedback
Based on whom the message is addressed
We classify communication according to the number of persons (receivers) to whom the message is addressed:
- Intrapersonal Communication:
- It is talking to oneself in one’s own mind. Examples are soliloquies or asides in dramatic works.
- Interpersonal Communication:
- It is the exchange of messages between two persons. For example, a conversation, dialogue, or an interview in which two persons interact (others may also be present as audience). An author communicates interpersonally with his reader, who is always present as a silent audience in the author’s mind while he writes. A letter too is an example of interpersonal communication between the writer and the person to whom it is written.
- Group Communication:
- It can be among small or large groups, like an organization, club or classroom, in which all individuals retain their individual identity.
- Mass Communication:
- It occurs when the message is sent to large groups of people, for example, by newspaper, radio, or television. In this process, each person becomes a faceless individual with almost no opportunity for personal response or feedback.
Based On the basis of the medium employed
- Verbal Communication:
- It means communicating with words, written or spoken. Verbal communication consists of speaking, listening, writing, reading, and thinking. It may further be classified as Oral or Written Communication.
- Non-verbal communication:
- It includes using of pictures, signs, gestures, and facial expressions for exchanging information between persons. It is done through sign language, action language, or object language. Non-verbal communication flows through all acts of speaking or writing. It is a wordless message conveyed through gestures (sign), movements (action language), and object language (pictures/clothes) and so on. Further non-verbal communication can be identified by personal space (proxemics), sense of smell (olfactics) and time (chronemics).
- Meta Communication:
- Here the speaker’s choice of words unintentionally communicates something more than what the actual words state. For example, a flattering remark like “I’ve never seen you so smartly dressed” could also mean that the regular attire of the listener needed improvement.
- Formal Communication:
- A formal channel of communication can be defined as a means of communication that is formally controlled by managers or people occupying positions in an organization. The communication flows through formal channels, that is, officially recognized positions along the line in the organization. This ensures that the information flows orderly, timely, and accurately. Any information, decision, memo, reminder etc. will follow this path.
- Informal Communication:
- Side by side with the formal channel of communication every organization has an equally effective channel of communication that is the informal channel. It is not officially sanctioned, and quite often it is even discouraged or looked down upon. But, then, it is very much there, and has been given the name ‘grapevine’ precisely because it runs in all directions-horizontal, vertical, diagonal. As the management experts put it, “it flows around water coolers, down hallways, through lunch rooms, and wherever people get together in groups”.
- Downward Communication:
- The Communication that flows from Top to Bottom is known as downward communication. Any organization has an inbuilt hierarchical system, and in that, in the first instance, communication invariably flows downwards.
- Upward Communication:
- The Communication that flows from bottom to top, which is from lower hierarchical level to higher level, is called Upward Communication. The main function of upward communication is to supply information to the upper levels about what is happening at the lower levels. It is just the reverse of the previous dimension
- Lateral Communication:
- When communication takes place between two or more persons who are subordinates working under the same person, or those who are working on the same level, it is called lateral or horizontal communication. A good example of this kind of communication is that between functional managers. It is necessary for the reviewing of the activities assigned to various subordinates having identical positions
- Diagonal Communication:
- Diagonal or Crosswise communication includes flow of information among persons at different levels who have no direct reporting relationships. As an example, the Communication between the Training Supervisor and Marketing Manager, regarding the Training of a few employees of Marketing Department, is Diagonal Communication. This kind of communication is used to speed up information flow, to improve understanding, and to coordinate efforts for the achievement of organizational objectives.
Objectives/Purpose Of Communication
The objectives of communication are dynamic and ever-changing. Some of the common objectives of official communication are to get or give information, to ask for or give instructions or advice or suggestions, to make requests, to persuade other people to agree with us. Sometimes, we communicate with the intention of complaining, or warning; but unfortunately, we do this angrily and get into arguments. If we learn to complain and warn in an acceptable and constructive manner, our serious intention can be conveyed quite effectively without damaging relationships. In order to caution, counsel, clarify, apprise, evaluate, reprimand, organize and numerous such objectives, we make use of communication.
Evaluation Of Communication Effectiveness
Communication is not an end in itself; rather it is a means to attain other ends or goals. Hence, it has to be effective to be able to attain these goals or objectives. Communication effectiveness can be examined in relation to the following criteria:
- Fidelity of Communication: the distortion free quality of a message is called fidelity. An effective person gets the message across to others with minimal possibilities of misunderstanding.
- Economy: In an effective communication a minimum of energy time, symbols and cues are used to encode message without losing its fidelity and impact.
- Congruence: An effective communication integrates both verbal and non-verbal cues.
- Influence: The most important criterion of effectiveness is the influence that the communicator is able to exercise over the receiver of the communication. Influence means the communicator achieve the results he intended.
- Relationship Building: An effective communication contributes to the building of trust and better relationship between the source and the target.
Seven C’s of Effective Communication:

These are the Seven terms, starting with the letter C, which make communication more understandable, valuable and effective.
UGC NET Communication study notes
Four S’s of Communication:
Four terms starting with letter S, which add to the value of the message in Communication
- Sincerity
- Simplicity
- Shortness
- Strength
LET US SUM UP:
Communication is defined as “the process of passing information and understanding from one person to another, it is essentially a bridge of meaning between people” All communication is essentially sharing of information or some message. Communication is the most important of our social activities. We can classify communication as interpersonal, intrapersonal, group communication, Meta communication, upward, downward, lateral, diagonal, formal, informal, oral, written or non verbal communication. Reading, writing, speaking and listening are the four skills of communication The objective of communication may to inform, to persuade, to train, to motivate, to educate, to relate, to reprimand, to rectify and so on.
· Theories and models of communication
· Barriers to Communication
· Organizational communication
· Formal communication channels and network Pro and Cons
· Organizational Communication channel network and Pro and Cons
Feedback in the communication process is the response that gives us some indication of how effectively we communicate. It is the gauge of efficiency in communication
Classification of Communication
RELATED POSTS
MCQ ON COMMUNICATION
BARRIERS TO COMMUNICATION | Study Material for UGC NET PAPER…



